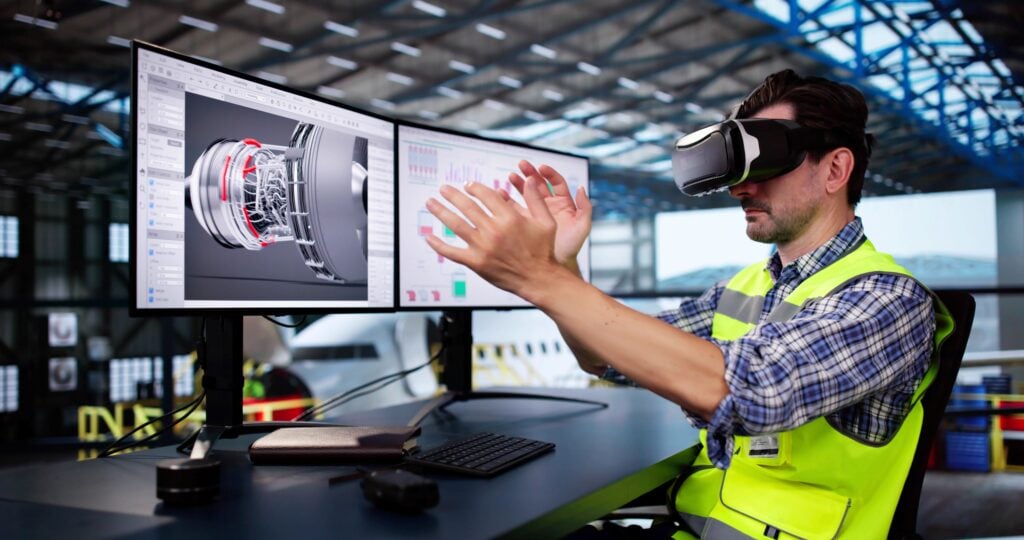
We live in an age where technological improvements to so many areas of our lives see the effect of such changes have an impact at an exponential level. In the aviation MRO industry, no longer are changes almost imperceptible in the whole scheme of things, instead these changes create major challenges where staff training is concerned. Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) operations are critical to ensuring safety, operational efficiency, and compliance with stringent regulatory standards. Today, the sector faces ongoing challenges—an ageing workforce, increasing aircraft complexity, and the urgent need to train new technicians efficiently without compromising quality. Emerging technologies such as Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) have now entered into the arena at a time when MRO staff are just coming to terms with the new skills and ongoing training required for working with new composite materials. These latest technologies are now poised to transform MRO training, making it more immersive, interactive, and cost-effective than ever before, so the question is, will they help staff to work with new materials and technologies, or will they simply become another field where specific knowledge is required to maximise the benefits?
1. The MRO Training Challenge
Traditional MRO training often relies on classroom-based theory, paper manuals, and occasional hands-on sessions using actual aircraft or components. While effective to a degree, this model is time-consuming, expensive, and limited by the availability of equipment. Furthermore, with global fleets expanding and new-generation aircraft entering service, the skills gap is widening—making accelerated yet high-quality training an industry imperative.
2. Why AR and VR are Game-Changers
AR and VR offer a fundamentally different approach to learning.
- Virtual Reality (VR) fully immerses trainees in a simulated 3D environment, enabling them to practise maintenance procedures on virtual aircraft without physical constraints.
- Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital information—such as 3D models, instructions, or diagnostics—onto the real-world view, allowing technicians to work with physical components while receiving guided digital assistance.
These tools bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical skills, offering safe, repeatable, and engaging training experiences.
3. Benefits of Immersive MRO Training
- Realistic Simulations Without Risk
VR allows technicians to practise high-risk or rare maintenance scenarios without endangering equipment or personnel. Mistakes become learning opportunities rather than costly setbacks.
- On-Demand and Scalable Learning
Trainees can access VR modules or AR-guided exercises anytime, anywhere, enabling consistent training across dispersed teams and reducing travel expenses.
- Enhanced Retention and Engagement
Studies indicate that immersive training can significantly improve memory retention and problem-solving skills compared to traditional methods, thanks to hands-on interaction and visual reinforcement.
- Reduced Downtime for Equipment
Since VR simulations do not require real aircraft to be grounded for training purposes, operational disruption is minimised.
4. Real-World Applications in MRO Training
Several aviation companies and training organisations are already integrating AR and VR into their MRO programmes.
- Engine Maintenance: VR environments allow trainees to dismantle and reassemble virtual engines repeatedly, mastering each step before handling actual hardware.
- AR Troubleshooting Guides: AR glasses or tablets can project step-by-step repair instructions onto physical components, reducing error rates and accelerating repair times.
- Regulatory Compliance Training: Simulations can replicate regulatory inspection procedures, ensuring technicians are prepared for real-world audits.
5. Overcoming Implementation Barriers
While the benefits are compelling, adopting AR and VR in MRO training comes with challenges:
- Initial Investment Costs: High-quality VR headsets, AR devices, and software development require upfront expenditure.
- Integration with Existing Curricula: Training organisations must ensure digital modules align with regulatory requirements and established learning pathways.
- Technological Familiarity: Both trainers and trainees may need an introduction to the hardware and software before fully benefiting from it.
6. The Road Ahead
As AR and VR hardware becomes more affordable and software more sophisticated, the barriers to adoption will become less of a problem. The integration of AI-driven adaptive learning could personalise training even further, while 5G connectivity will enable real-time data streaming for remote AR assistance.
For an industry where precision, safety, and efficiency are paramount, immersive training could become not just an enhancement but a necessity. In the coming decade, the MRO workforce may be trained predominantly through virtual hangars, AR-guided inspections, and AI-driven skill assessments—ushering in a new era of aviation maintenance excellence.